Default Settings
After defining the Server Name, Webmaster email address, and Available Addresses, click the Virtual Hosts tab and click the Edit Default Settings button. The window shown in Figure 13-3 will appear. Configure the default settings for your Web server in this window. If you add a virtual host, the settings you configure for the virtual host take precedence for that virtual host. For a directive not defined within the virtual host settings, the default value is used.
Site Configuration
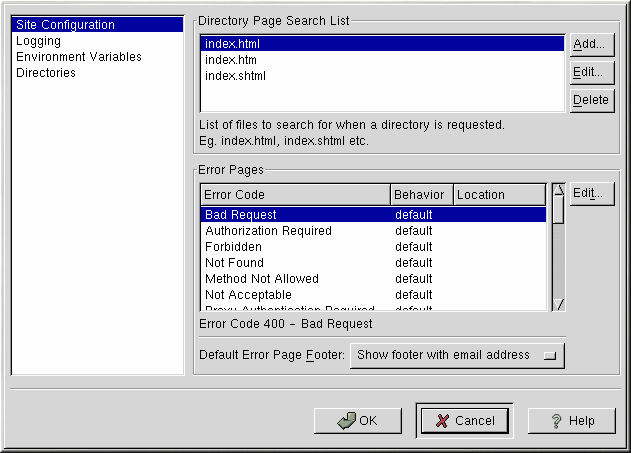
The default values for the Directory Page Search List and Error Pages will work for most servers. If you are unsure of these settings, do not modify them.
The entries listed in the Directory Page Search List define the DirectoryIndex directive. The DirectoryIndex is the default page served by the server when a user requests an index of a directory by specifying a forward slash (/) at the end of the directory name.
For example, when a user requests the page http://your_domain/this_directory/, they are going to get either the DirectoryIndex page if it exists, or a server-generated directory list. The server will try to find one of the files listed in the DirectoryIndex directive and will return the first one it finds. If it does not find any of these files and if Options Indexes is set for that directory, the server will generate and return a list, in HTML format, of the subdirectories and files in the directory.
Use the Error Code section to configure Apache to redirect the client to a local or external URL if the event of a problem or error. This option corresponds to the ErrorDocument directive. If a problem or error occurs when a client tries to connect to the Apache Web server, the default action is to display the short error message shown in the Error Code column. To override this default configuration, select the error code and click the Edit button. Choose Default to display the default short error message. Choose URL to redirect the client to an external URL and enter a complete URL including the http:// in the Location field. Choose File to redirect the client to an internal URL and enter a file location under the document root for the Web server. The location must begin the a slash (/) and be relative to the Document Root.
For example, to redirect a 404 Not Found error code to a Web page that you created in a file called 404.html, copy 404.html to DocumentRoot/errors/404.html. In this case, DocumentRoot is the Document Root directory that you have defined (the default is /var/www/html). Then, choose File as the Behavior for 404 - Not Found error code and enter /errors/404.html as the Location.
From the Default Error Page Footer menu, you can choose one of the following options:
Show footer with email address — Display the default Apache footer at the bottom of all error pages along with the email address of the website maintainer specified by the ServerAdmin directive. Refer to the Section called General Options for information about configuring the ServerAdmin directive.
Show footer — Display just the default Apache footer at the bottom of error pages.
No footer — Do not display a footer at the bottom of error pages.
Logging
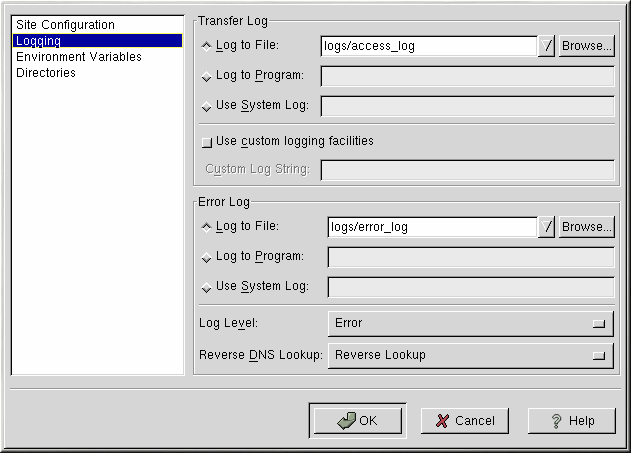
By default, Apache writes the transfer log to the file /var/log/httpd/access_log and the error log to the file /var/log/httpd/error_log.
The transfer log contains a list of all attempts to access the Web server. It records the IP address of the client that is attempting to connect, the date and time of the attempt, and the file on the Web server that it is trying to retrieve. Enter the name of the path and file in which to store this information. If the path and filename does not start with a slash (/), the path is relative to the server root directory as configured. This option corresponds to the TransferLog directive.
You can configure a custom log format by checking Use custom logging facilities and entering a custom log string in the Custom Log String field. This configures the LogFormat directive. Refer to http://httpd.apache.org/docs/mod/mod_log_config.html#formats for details on the format of this directive.
The error log contains a list of any server errors that occur. Enter the name of the path and file in which to store this information. If the path and filename does not start with a slash (/), the path is relative to the server root directory as configured. This option corresponds to the ErrorLog directive.
Use the Log Level menu to set how verbose the error messages in the error logs will be. It can be set (from least verbose to most verbose) to emerg, alert, crit, error, warn, notice, info or debug. This option corresponds to the LogLevel directive.
The value chosen with the Reverse DNS Lookup menu defines the HostnameLookups directive. Choosing No Reverse Lookup sets the value to off. Choosing Reverse Lookup sets the value to on. Choosing Double Reverse Lookup sets the value to double.
If you choose Reverse Lookup, your server will automatically resolve the IP address for each connection which requests a document from your Web server. Resolving the IP address means that your server will make one or more connections to the DNS in order to find out the hostname that corresponds to a particular IP address.
If you choose Double Reverse Lookup, your server will perform a double-reverse DNS. In other words, after a reverse lookup is performed, a forward lookup is performed on the result. At least one of the IP addresses in the forward lookup must match the address from the first reverse lookup.
Generally, you should leave this option set to No Reverse Lookup, because the DNS requests add a load to your server and may slow it down. If your server is busy, the effects of trying to perform these reverse lookups or double reverse lookups may be quite noticeable.
Reverse lookups and double reverse lookups are also an issue for the Internet as a whole. All of the individual connections made to look up each hostname add up. Therefore, for your own Web server's benefit, as well as for the Internet's benefit, you should leave this option set to No Reverse Lookup.
Environment Variables
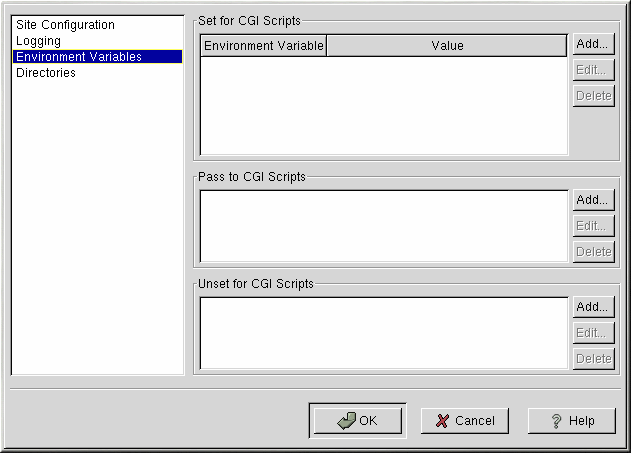
Apache can use the mod_env module to configure the environment variables which are passed to CGI scripts and SSI pages. Use the Environment Variables page to configure the directives for this Apache module.
Use the Set for CGI Scripts section to set an environment variable that is passed to CGI scripts and SSI pages. For example, to set the environment variable MAXNUM to 50, click the Add button inside the Set for CGI Script section as shown in the Section called Environment Variables and type MAXNUM in the Environment Variable text field and 50 in the Value to set text field. Click OK. The Set for CGI Scripts section configures the SetEnv directive.
Use the Pass to CGI Scripts section to pass the value of an environment variable when Apache was first started to CGI scripts. To see this environment variable, type the command env at a shell prompt. Click the Add button inside the Pass to CGI Scripts section and enter the name of the environment variable in the resulting dialog box. Click OK. The Pass to CGI Scripts section configures the PassEnv directive.
If you want to remove an environment variable so that the value is not passed to CGI scripts and SSI pages, use the Unset for CGI Scripts section. Click Add in the Unset for CGI Scripts section, and enter the name of the environment variable to unset. This corresponds to the UnsetEnv directive.
Directories
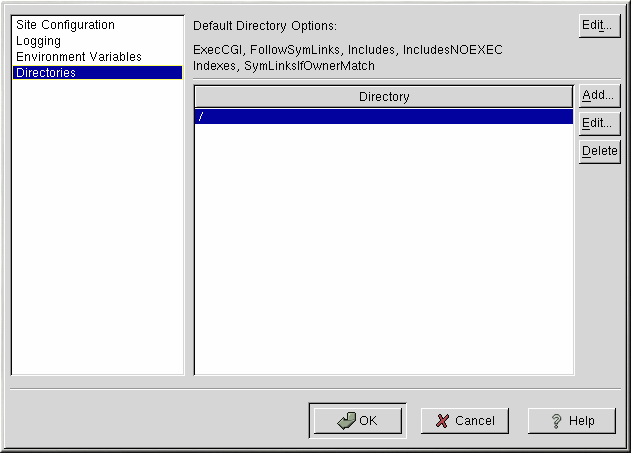
Use the Directories page to configure options for specific directories. This corresponds to the <Directory> directive.
Click the Edit button in the top right-hand corner to configure the Default Directory Options for all directories that are not specified in the Directory list below it. The options that you choose are listed as the Options directive within the <Directory> directive. You can configure the following options:
ExecCGI — Allow execution of CGI scripts. CGI scripts are not executed if this option is not chosen.
FollowSymLinks — Allow symbolic links to be followed.
Includes — Allow server-side includes.
IncludesNOEXEC — Allow server-side includes, but disable the #exec and #include commands in CGI scripts.
Indexes — Display a formatted list of the directory's contents, if no DirectoryIndex (such as index.html) exists in the requested directory.
Multiview — Support content-negotiated multiviews; this option is disabled by default.
SymLinksIfOwnerMatch — Only follow symbolic links if the target file or directory has the same owner as the link.
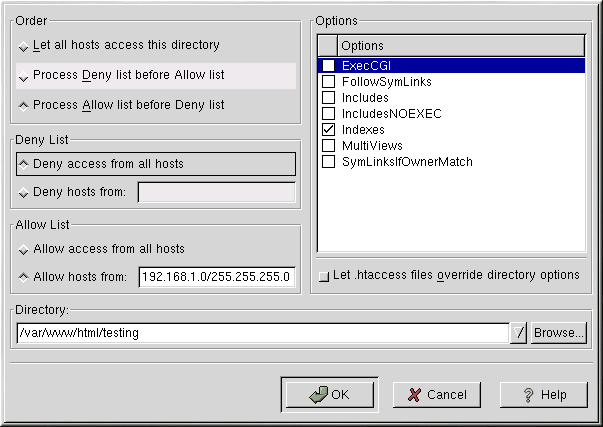
To specify options for specific directories, click the Add button beside the Directory list box. The window shown in Figure 13-7 appears. Enter the directory to configure in the Directory text field at the bottom of the window. Select the options in the right-hand list, and configure the Order directive with the left-hand side options. The Order directive controls the order in which allow and deny directives are evaluated. In the Allow hosts from and Deny hosts from text field, you can specify one of the following:
Allow all hosts — Type all to allow access to all hosts.
Partial domain name — Allow all hosts whose names match or end with the specified string.
Full IP address — Allow access to a specific IP address.
A subnet — Such as 192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0
A network CIDR specification — such as 10.3.0.0/16
If you check the Let .htaccess files override directory options, the configuration directives in the .htaccess file take precedence.